Introduction
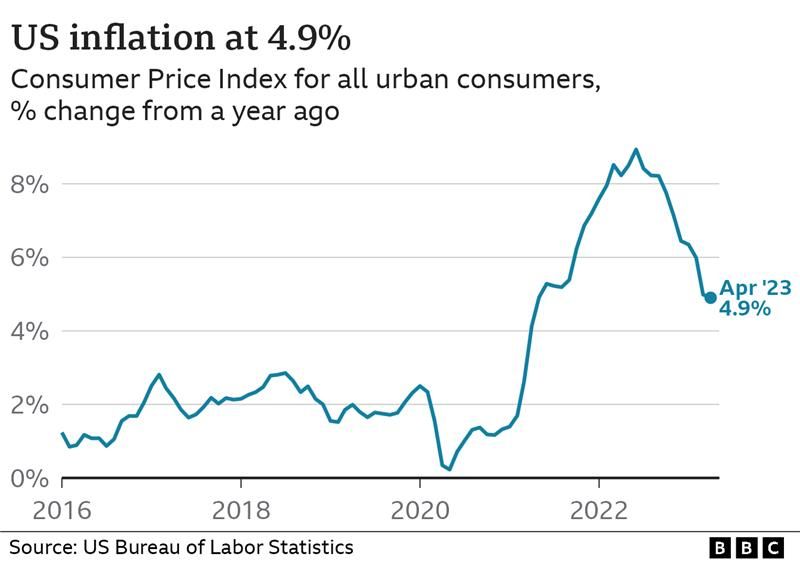
Inflation in the United States has been on the rise for the past two years, but recent data suggests that it may be losing some of its momentum. The June 2023 Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose by 3% year-over-year, which is the smallest increase since March 2021. While this is good news for consumers, it does not necessarily indicate that inflation is over. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind the diminishing impact of inflation, the factors that may contribute to its resurgence, and the future outlook.
The Impact of Federal Reserve's Actions
Rising Interest Rates as a Cooling Measure
One of the key factors contributing to the diminishing punch of inflation is the Federal Reserve's proactive approach to cool down the economy. The Fed has been gradually raising interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest. As a result, businesses are less likely to raise prices, which helps to keep inflation in check. By using this monetary policy tool, the Federal Reserve aims to strike a balance between economic growth and price stability.
Easing of Supply Chain Disruptions
Another significant factor in the current trend is the easing of supply chain disruptions. In 2022, supply chains were heavily impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic and related restrictions. However, as COVID-19 restrictions in China and other parts of the world begin to ease, global trade has improved, leading to a gradual easing of these disruptions. As supply chains stabilize and regain their efficiency, prices for goods and services are expected to normalize, contributing to the moderation of inflation.
Potential Risks for Inflation Resurgence
Energy Price Volatility due to the War in Ukraine
While there are positive indications of inflation losing its punch, there are also risks that could lead to its resurgence. The ongoing war in Ukraine has the potential to cause energy prices to rise significantly. Energy is a critical input in various sectors, and if energy prices continue to escalate, it could exert upward pressure on inflation. Monitoring the geopolitical situation and its impact on energy markets will be essential to understanding the potential risks to inflation in the United States.
The Pace of Interest Rate Adjustments
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in managing inflation through its monetary policy decisions. However, if the Fed fails to raise interest rates sufficiently, it could allow inflation to get out of control. Insufficient rate adjustments could erode the value of people's savings and make it more challenging for businesses to borrow money, potentially exacerbating inflationary pressures. Striking the right balance with interest rate adjustments will be critical in keeping inflation in check.
Additional Factors Influencing Future Inflation
In addition to the above-mentioned factors, several other variables can affect inflation in the future. These factors include:
1. The Pace of Economic Growth
If the economy experiences rapid growth, it can lead to increased demand for goods and services. This heightened demand can push prices up, potentially reigniting inflationary pressures. Monitoring economic growth and ensuring it remains balanced will be crucial for managing inflation.
2. The Labor Market Dynamics
Tightening labor markets can provide workers with increased bargaining power, leading to higher wages. Higher wages, in turn, can contribute to higher production costs and ultimately result in higher prices for goods and services. Understanding labor market conditions and their impact on inflation is essential for effective inflation management.
3. The Stability of the Stock Market
The stock market can significantly influence consumer confidence and spending patterns. If the stock market crashes or experiences significant volatility, it can lead to a decline in consumer confidence. This decline in confidence may result in reduced spending, which can contribute to lower inflation levels. Keeping a close eye on stock market trends can provide insights into potential inflationary risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q: Is the recent decrease in inflation a positive sign for the economy?
- A: The recent decrease in inflation is indeed good news for consumers. It indicates that price pressures are moderating. However, it does not necessarily imply that inflation is completely over. Monitoring future trends and economic indicators will provide a clearer picture.
- Q: How does the Federal Reserve control inflation?
- A: The Federal Reserve controls inflation through various monetary policy tools. One of the key tools is adjusting interest rates. By raising interest rates, the Fed aims to make borrowing more expensive, thereby reducing spending and curbing inflationary pressures.
- Q: Can the war in Ukraine have a significant impact on inflation in the United States?
- A: Yes, the war in Ukraine has the potential to impact inflation in the United States. Energy prices, a major input for many goods and services, can be influenced by geopolitical tensions. Rising energy prices can contribute to higher inflation.
- Q: How does economic growth affect inflation?
- A: Rapid economic growth can lead to increased demand for goods and services, which can push prices higher. Sustained and balanced economic growth is crucial to managing inflation effectively.
- Q: How do labor market dynamics influence inflation?
- A: Tight labor markets can give workers more bargaining power, resulting in higher wages. Increased wages can lead to higher production costs, which may translate into higher prices for goods and services.
- Q: Why is monitoring the stock market important for managing inflation?
- A: The stock market plays a significant role in shaping consumer confidence. A crash or significant volatility in the stock market can lead to a decline in consumer confidence, potentially resulting in lower spending and lower inflation.
Conclusion
Inflation in the United States has shown signs of losing its punch, with the recent data indicating a moderation in price increases. Factors such as the Federal Reserve's interest rate adjustments and the easing of supply chain disruptions have contributed to this trend. However, potential risks, including energy price volatility and the pace of interest rate adjustments, need to be closely monitored to ensure inflation remains under control. Additionally, factors like economic growth, labor market dynamics, and stock market stability can also influence inflationary pressures. Understanding and managing these factors will be essential in navigating the complex issue of inflation in the United States.